What is an otoscope used for?
Otoscope is a laparoscopic instrument for examination or surgical evaluation of the external ear canal, tympanic membrane, middle ear, etc. The ear endoscope can observe the parts that are not easily observed by the operating microscope, such as the upper thigh chamber and the posterior thigh chamber, so as to find the middle ear disease in time and reduce the recurrence rate of the disease. The advantage lies in non-invasiveness, high resolution of images in the ear, high lighting function, and high diagnosis rate, which enables clinicians to grasp the specific subtle lesions in the ear and provide patients with timely treatment plans.
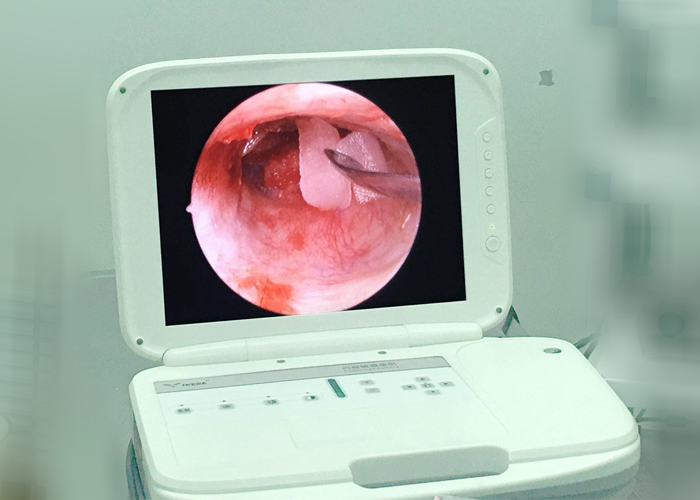
Clinical application of otoscope:
1. Take cerumen (earwax), foreign body in the external auditory canal.
2. Take a biopsy.
3. Tympanic membrane puncture.
4. External auditory canal medication.
5. Ear disease examination: acute suppurative otitis media, chronic suppurative otitis media, catarrhal otitis media, tinnitus, sudden deafness, etc.
Operation process of otoscope examination:
1. Prepare items before inspection and treatment to ensure the normal operation of various instruments.
2. To connect the instrument, first connect the light guide, the endoscope camera, the power cord, the mirror, etc., and then turn it on after everything is connected to better protect the machine. Avoid folding and twisting of optical fiber to ensure smooth suction of negative pressure.
3. After powering on, you need to do white balance first, aim the mirror at the gauze or white paper 90 degrees vertically, and press and hold the white balance button on the camera or panel for 3-4 seconds.
4. Assist the patient to take the supine head tilted to one side or the contralateral side (the affected ear is facing upwards).
5. For patients with hard cerumen in the external auditory canal, soften the cerumen first.
6. Assist the doctor to apply 2~3 drops of 1%~2% tetracaine to the ear for local infiltration anesthesia.
7. During the puncture, the patient's head and body should not be shaken to ensure it is fixed.
8. Observe closely whether the patient has any adverse reactions, and ask how the patient feels.
9. After the operation, gently plug the external auditory canal with a sterile cotton ball.
10. Arrange the supplies and turn off the instrument.