Uterine fibroids are the most common benign tumors of female reproductive organs, and the most commonly used treatment is laparoscopic myomectomy. Hysteromyomectomy not only preserves the patient's fertility, but more importantly, it maintains the physiological function of the uterus, maintains the integrity of the anatomical structure of the pelvic floor, and has the least impact on the hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian-uterine axis, which is beneficial Physical and mental health of patients after surgery.
Indications of laparoscopic myomectomy
1. Medium-sized (diameter <9cm) subserosal uterine fibroids;
2. Intermural uterine fibroids of medium size (diameter <9cm), and the number of fibroids should not exceed 3;
3. Posterior uterine fibroids and intermural fibroids embedded in the muscle layer may be considered for myomectomy, but the surgeon must have a good laparoscopic suture technique. In addition, the surgeon should perform ultrasound and hysteroscopy before surgery to understand the growth location, size and number of fibroids, which is necessary to determine whether to perform surgery. For submucosal fibroids in the uterine cavity, hysteroscopic myomectomy may be more appropriate.
The process of laparoscopic myomectomy:
1. Anesthesia: A professional anesthetist will anaesthetize the patient, and the patient can undergo a full-course painless treatment, which reduces the physical and psychological pain caused by the operation.
2. Punching: Doctors do not need to cut the patient's belly like traditional surgery, but poke three thin "instrument hands" into the patient's abdomen. Because the incision is very small, the chance of surgical infection is greatly reduced, and patients do not need to inject large amounts of antibiotics for a long time after surgery.
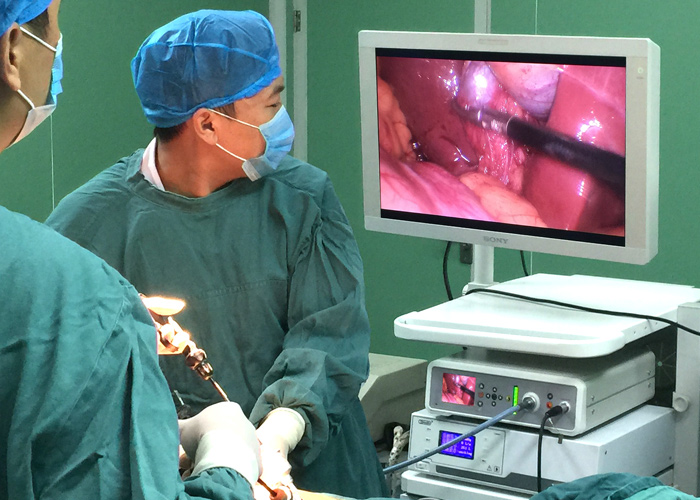
3. Observation by medical monitor
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgery. The images reflecting the endoscopic conditions of the organs are transmitted through the endoscopic camera. Through the medical monitor, the doctor can observe the clear and detailed intracavitary tissues, and at the same time use the abdominal cavity operation instruments to complete various difficult tasks Operation.
4. Incision of the myometrium
5. Perform peeling of uterine fibroids
After uterine fibroids are removed, the wounds often bleed severely. Therefore, skilled uterine fibroids peeling technology is the key, which can make other normal tissues of the patient’s uterus suffer as little damage as possible. For pedicled subserous uterine fibroids, laparoscopy is Most suitable.
6. Suture under laparoscopy
Laparoscopic suturing techniques require intensive practice. After uterine fibroids are removed, the wound often bleeds severely, and coagulation to stop the bleeding cannot be effective, and rapid suturing must be used.
7. Remove the fibroids
Take out the uterine fibroids with a tumor crusher, flush the abdominal cavity, check that the incision does not ooze blood, finally empty the abdominal cavity, pull out the instruments, and the operation is over.
Incision of the myometrium, removing fibroids, suturing the uterine incision, and removing the fibroids, these four steps are technically difficult to operate, and some special problems related to these operations may occur. Therefore, uterine fibroids under laparoscopic surgery Elimination has the following basic principles:
(1) The principle of minimally invasive surgery must be mastered: avoid abdominal infections, use sophisticated and non-invasive instruments, and do not touch any organs in the pelvic cavity except for uterine fibroids, and perform gentle and non-invasive operations on the uterus.
(2) Each fibroids must be removed individually: the uterine fibroids cannot be removed with an open surgery, and as many uterine fibroids are removed through a uterine incision.
(3) The fibroids must be separated along the interface between the fibroids and the adjacent muscle layer: the pseudo-capsule composed of compressed muscle fibers and turned uterine blood vessels makes the dividing surface clear, so as to preserve the adjacent normal muscle layer and avoid damage Due to the compression of uterine fibroids, the blood vessels surrounding the fibroids have been expanded and may be the source of massive bleeding.
(4) Minimize the use of electrocoagulation: After uterine fibroids are removed, in order to achieve hemostasis at the incision, electrocoagulation must be used as little as possible.
(5) Requirements for suture of uterine incision: Any technical defect may cause uterine rupture during pregnancy after surgery, so the following points must be paid attention to when suture of uterine incision: ①Except for pedicled uterine fibroids, other uterine fibroids The resection site must be sutured; ②The full thickness of the uterine incision must be sutured, so as to avoid the formation of deep hematoma in the muscle layer after the operation. This hematoma can weaken the scar tissue and may cause fistula formation; ③When entering the uterus When the myometrium defect is deep after the cavity or uterine fibroids are removed, it needs to be sutured in two layers. This suture can also be completed under laparoscopy; ④If it is difficult to suture the uterine incision, you should use laparoscopy without hesitation In uterine myomectomy, a laparoscope is used to expose the fibroids, start or complete the enucleation of the fibroids, and then suture the uterine incision through a small incision in the abdominal wall in the traditional way.
Complications of laparoscopic myomectomy
(1) The unique complications of laparoscopic surgery
1. Complications related to pneumoperitoneum. Such as hypercapnia, subcutaneous emphysema, gas embolism and so on.
2. Complications related to abdominal puncture. Such as intra-abdominal cavity or substantial organ damage, retroperitoneal large vessel damage, etc., a puncture hernia herniated through a puncture hole should also be attributed to such complications.
3. Complications caused by performance defects or improper use of special surgical instruments for laparoscopy, such as ischemic stenosis of the bile duct caused by electric heating, and perforation of hollow organs caused by the "skin effect" of high-frequency current.
(2) Traditional complications of laparoscopic surgery
Such complications are essentially the same as those of traditional surgical procedures, but their causes, probability, severity, treatment methods and outcomes are not the same, such as incision and intra-abdominal infection, post-tumor surgery Intra-abdominal or abdominal wall implantation, bile duct injury, postoperative bleeding, etc.